ANA (AntiNuclear Antibody) Test
ANA (AntiNuclear Antibody) test is used as one of the tests to diagnose Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease. SLE affects females more commonly than males. It is a systemic disease and can affect almost every part of the body. There is no single specific cause of SLE but environmental and genetic factors and drug reactions have a causative link. ANAs are auto antibodies against various cell nucleus proteins (antigens). The antibodies that are characteristic of SLE are directed against Deoxyribo nucleoprotein (DNP).
Principle:
It is an agglutination test. When the test serum (containing antinuclear antibodies) is brought into contact with latex particles coated with DNP (Deoxyribo nucleoprotein), agglutination of the latex particles takes place indicating a positive reaction.
Requirements:
- Serum sample
- SLE latex reagent
- Positive and negative controls (PC; NC)
- Test card
- Normal saline
- Disposable mixing sticks
- Mechanical rotator (80-100 rpm)
- Test tubes
Procedure:
- Bring the kit reagents and sample to room temperature.
- Place 0.05 ml of the serum into one circle of slide.
- Place similar quantities of positive and negative controls in separate circles.
- Gently mix the latex reagent vial (to ensure homogeneity) and place one drop to each of the circle.
- Mix the contents of each circle evenly with disposable sticks and spread over the complete area of the circle.
- Place the slide on mechanical rotator for 2 minutes (80-100 rpm).
- Examine for agglutination macroscopically.
- Compare the results with positive and negative controls.
Results:
- Agglutination indicates a positive reaction while a negative reaction is indicated by the absence of agglutination.
Semi Quantitative Test:
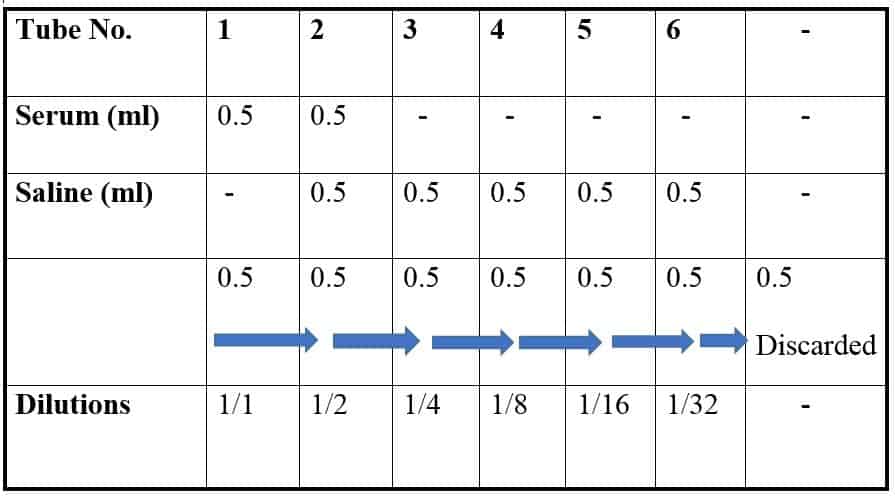
- If the test is positive, serial dilutions of the serum are tested.
- The highest dilution of the serum giving positive result will be the titre.
- Prepare double dilutions of serum as follows:
Quality Control:
- Positive and negative controls (animal serum in sodium azide) are included in the kit and must be run parallel to every test performed.
Interpretation of ANA Test:
- The test is not entirely specific and becomes positive in:
-
-
- Systemic sclerosis
- Sjögren’s syndrome
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Dermatomyositis
- Tuberculosis
- Lymphoma
-
- About 10% of the normal healthy population has antinuclear antibodies which are undetectable.
- 95% of the patients with SLE have a positive ANA test result.