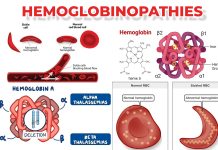
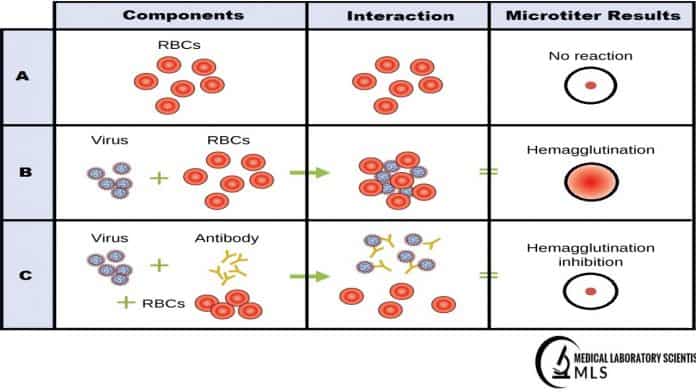
Haemagglutionation test detect the presence of viral particles and can see visibly and macroscopically. This test does not distinguish between the viral particles which are infectious and these particles are degraded and no longer and capable to infect the cells. Both may cause the agglutination of RBCs. Substances which can agglutinate RBCs are known as Haemagglutinins. Haemagglutionation assay was initially developed in 1941-42 by American Virologist name George Hirst. It is method, which is used for the quantification and concentration of bacteria and viruses.
Principal:
The main principal behind this assay, the Nana Receptors which are present on RBCs, come in contact with Haemagglutinins Neuraminidase – HN, a protein receptor which are present on the virus’s surface. This mixture/combination form a complex between virus and RBCs as Virus+RBCs, which prevent or stop the RBCs to settling down with the passage of time. As a result agglutinate become visible as a precipitate of red blood cells in the well of kit plate.
Material and Equipment:
- Macro and micropipette
- Normal saline or Phosphate Buffer Solution – PBS
- EDTA Vial
- Washed Red Blood Cells – RBCs (Taken from Chicken, Rabbit or Sheep)
- Virus particles or Vaccine
- Centrifuge machine
- Falcon Tubes
- Well plate 96
- Yellow tips
Preparation of Red Blood Cells – RBCs:
- Take chicken blood in a test tube and mix gently.
- Add 4 to 5 Micro litter of PBS or Normal saline and mix.
- Centrifuge the test tube at speed 3000RPM for 2 to 3 min.
- After the centrifugation break the button or pallet which is form at the bottom of test tube and discard the supernatant.
- Repeat this process for at least 2 to 3 times.
- After the final washing prepare the 5% stock solution.
- Take 1 drop of washed red blood cells in test tubes and add 19 drops of normal saline.
Procedure:
Dilute the virus sample by adding exact quantity of distilled water with vaccine or virus particles.
- Take 96 well plate and mark it properly.
- Add 50 micro litter normal saline in each wellhorizontally in 12 wells.
- Put 50 micro litter of virus sample in 1stwell and mix with micro pipette.
- Now total quantity in 1st well is 100micro litter, take 50 micro litter with the help of pipette and transfer it in2nd well.
- Make serial dilution till 11th well andtake 50 micro litter from 11th well and discard it.
- The 12th wall has taken as Negative Control.
- Add 50 micro litter RBCs suspension in each wellsand mix it well.
- Incubate the plate at 37°C for at least 30 to 35 min.
- After incubation readthe results.
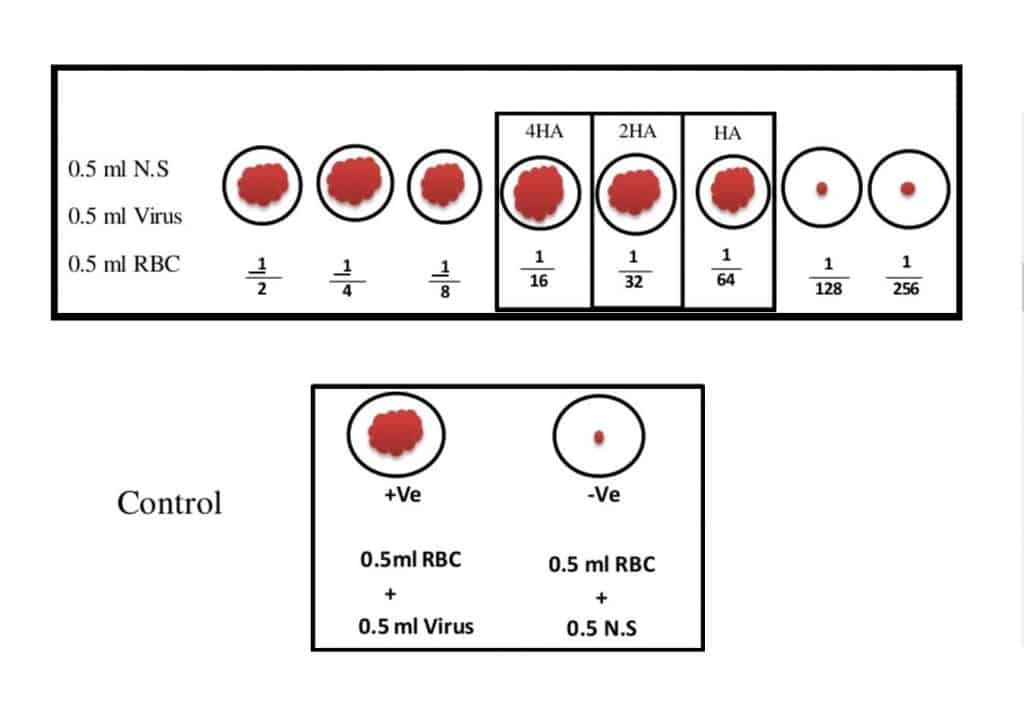
Interpretation and Results:
Afterthe incubation process, see the plate for visual analysis or macroscopically.
Positive Control:
At the bottom of the tube there is no pallet orbutton formation so there will be no RBCs settling down.
Negative Control:
There is clear settling down of RBCs and formation of pallet at the bottom of the tube.
Haemagglutionation Titer Level:
It is the reciprocal of the highest dilution of virus that will agglutinate the red blood cells.
OR
Viral dilution prevent the red blood cells settling down.